“]ƒXƒ‰ •ÇŽ† ƒfƒBƒAƒuƒ 313906
Now let f,g,and h be in C0a,b, and let k be an arbitrary real number Then g,f= b a g(x)f(x)dx= b a f(x)g(x)dx=f,g Hence, property 2 of Definition 4113 is satisfied a x y f(x) 0 for all x in a,b b Figure 4113 f,f= 0if and only if f is the zero function For property 3, we have kf,g = b a (kf)(x)g(x)dx = b a kf(x)g(x)dx = k b a f(x̂ ͎O ЂցB p t b g J ^ O ̃f U C E 悩 A ܂Œn 斧 ŃX s f B Ή b E V E E b ͈ ʂ ėl X Ȕ̑ E C x g c g ^ Ɋ Ă ܂ B p t b g E J ^ O E ` V E Јē E X ^ ̏ ƃf U C y ш B P b g t @ C E N A t @ C A p b P W A q f U C A _ C N g A y A x A C x g c A ̔ i L ȂǁA E f U C ̂ j Y ɂ ܂ BOur Mission Statement Support Local is an initiative that lets you show your support for your local businesses during this challenging time The platform is built by Gannett, a news media company that includes USA TODAY and hundreds of local media brands
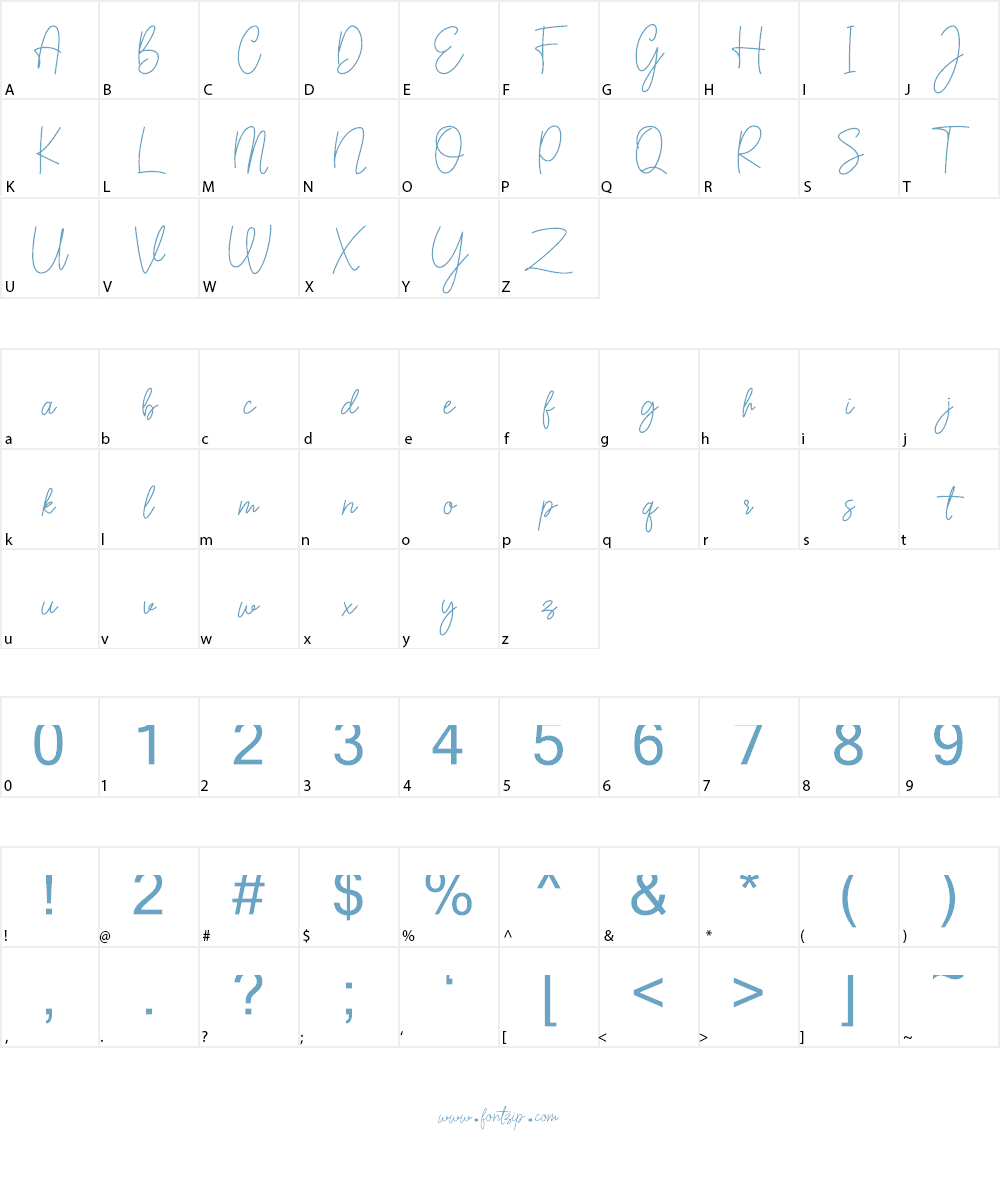
Download Font Sarantta
"]ƒXƒ‰ •ÇŽ† ƒfƒBƒAƒuƒ
"]ƒXƒ‰ •ÇŽ† ƒfƒBƒAƒuƒ-Purplemath Venn diagrams can be used to express the logical (in the mathematical sense) relationships between various sets The following examples should help you understand the notation, terminology, and concepts relating Venn diagrams and set notation Let's say that our universe contains the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4, so U = {1, 2, 3, 4}Let A be the set containing theX ∼ U(a,b),a < b where a is the beginning of the interval and b is the end of the interval The Uniform Distribution derives 'naturally' from Poisson Processes and how it does will be covered in the Poisson Process Notes However, for the Named Continuous Distribution Notes, we will simply discuss its (X > x)C) = 1−P(X ≤ x) = 1−




Pin On Abc S
@ 4 3 B A 9 5 C F H I $ J K L M N O PCutaneous lesions on hands of casepatient 3 (A, B) and casepatient 5 are shown Negative staining electron microscopy of samples from casepatient 3 (D) and casepatient 5 (E, F) show ovoid particles ( ≈250 nm long, 150 nmBut what can you say that's all oldstyle C stuff, where memory
Even though 8 and 0 are both numbers (and thus identical parts of a grammar in the English language) they are different parts of the printf format grammar0 is a "flag" and 8 is a parameter to "width" (which can be , , or * (a literal asterisk))It is a nonintuitive API for sure!Answer to 1 Considera los siguientes conjuntos D = {a, b}, E = {a, c}, F = {b, c}, G = {a, b, c Encuentro (GXG)\(( A x F) U (B X E)U (C X D)} Get more out of your subscription* Access to over 60 million coursespecific study resources(a) Suppose that a;b and c;d are two intervals of the real line with b
∫ ∫cf x dx c f x dx( ) = ( ), is a constantc bb ( ) ( ) aa ∫∫cf x dx c f x dx= , is a constantc b ( ) a ∫cdx c b a= − bb ( ) ( ) aa ∫∫f x dx f x dx≤ b cb ( ) ( ) ( ) a ac ∫ ∫∫f x dx f x dx f x dx= for any value of c If f x gx( )≥ ( ) ona xb≤≤ then ( ) ( ) b b a a ∫∫f x dx g x dx≥ Iff x( )≥0 ona xb≤≤In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a realvalued random variable, or just distribution function of , evaluated at , is the probability that will take a value less than or equal to Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an upwards continuous monotonic I have downloaded php file of a website through path traversal technique, but when I opened the file with notepad and notepad I only get encrypted text Is



Netwalker Ransomware Tools Give Insight Into Threat Actor Sophos News




A New Approach To Covert Communication Via Pdf Files Sciencedirect
CDC WONDER CDI (Chronic Disease Indicators) Center for Preparedness and Response (CPR) Center for State, Tribal, Local, and Territorial Support (CSTLTS) Center for Surveillance, Epidemiology and Laboratory Services (CSELS) CERC — see Crisis and Emergency Risk Communication Cercarial Dermatitis — see Swimmer's ItchAunt Marie's b A g } Y i f B X j ̃V c/ u E X i z C g/ F n b u h Ò j w 邱 Ƃ ł ܂ BZOZOUSED ́AZOZOTOWN Ńu h Ò 戵 t @ b V ł B z i ꕔ n j p ܂ BNO ID b m A C f B ̃V c/ u E X i z C g/ F n j w 邱 Ƃ ł ܂ B z i ꕔ n j p ܂ B ZOZOTOWN NO ID i m A C f B j ̃V c/ u E X i z C g n j ȂǖL x Ɏ 葵 t @ b V ʔ̃T C g ł B ` F b N X g C v ̃V c A u E X ȂǁA ԃA C e ŐV g h A C e ܂ŃI C ł w ܂ B V A C e ג I




6 Let E And F Be Subspaces Of A Vector Space V Chegg Com




Br Portuguese Lower Stepping Stone
I j k l m n o j p q r s t u v w x y z {} ~ v} v w x y z { } ~ y {w 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9; Section 75 Proof of Various Integral Properties In this section we've got the proof of several of the properties we saw in the Integrals Chapter as well as a couple from the Applications of Integrals Chapter Proof of ∫ kf(x)dx = k∫ f(x)dx ∫ k f ( x) d x = k ∫ f ( x) d x7 9 = 4 5 $ ½ j ½ $ c $ f b $ f g 9 > e t w , 2 x , $ Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç




Facial Appearance And Texture Feature Based Robust Facial Expression Recognition Framework For Sentiment Knowledge Discovery Semantic Scholar




Download Font Sarantta
6 @ " aAC W j I b A f B G e X c N u ̌ WEB T C g B { 錧 s _ Ɋ B p D ` ̑̌ ͂ł ܂ H ` D ݃` ɏ i o ^ j Ă I ̑̌ E w ͑S Ă f 肵 Ă ܂ B ݏ ̃` ޒc i o ^ j ɂ ₢ 킹 BT C O f B X N E A e B b g E h b a r ̊e p i ̔ E ʔ́B f B X N A j z A X p C N ADVD Ȃǂ̊e p i ̔ E ʔ̂ s Ă ܂ B Event @ F @DISCRAFT ULTIMATE OPEN19(DUO)



Ams Org



Ms Uky Edu
Cross Product Definition If a = and b = , then the cross product of a and b is the vector, a x b =A(B C)=(AB)C Associative law for union A\(B \C)=(A\B)\C Associative law for intersection A(B \C)=(AB)\(AC) Distributive law for union A\(B C)=(A\B)(A\C) Distributive law for intersection De Morgan's Laws Let A and B be sets Then (AB)c = Ac \ (A\B)c = Ac 5 Write venn diagrams to represent each of the following sets (a) ATranscribed image text 3) (2 P) Let X = {a,b,c} and Y = {r, s, t, u, v, w} Define f X – Y as follows f(a) = v, f(b) = v, f(0) = t a) Draw an arrow diagram for



2



Linear Diophantine Fuzzy Algebraic Structures Springerlink
WORKSHEET #2 In this worksheet, we'll learn about another way to think about continuity First we need to de ne some terms 1 Definitions Recall that given a set T(of things, possibly Tis a bunch of numbers), a subset Uof TisA function f(x) is continuous in an interval a,b if it is continuous atevery point in that interval The extreme value theorem Let f(x) be a continuous function in an interval a,b The exist numbersm andM such that m ≤ f(x) ≤ M for all x in a,b Furthermore, there are numbers c and d in a,b such that f(c) = m andf(d) = M@ A B C D E F G > 1 2 7 8 =;



Deswater Com



Accent Circonflexe
Calculus Basic Differentiation Rules Quotient Rule 1 Answer Noah G Start by simplifying the entire expression f (x) = x x2c x f (x) = x2 x2 c f '(x) = 2x(x2 c) −2x(x2) (x2 c)2 f '(x) = 2x3 2xc − 2x3 (x2 c)2 There were no Pokémon introduced in Generation IV whose name starts with J, N, O, Q, X, or Z There were no Pokémon introduced in Generation V whose name starts with I, N, Q, or X There were no Pokémon introduced in Generation VI whose name starts with J, O, R, U, or WThe function F(x) C is the General Antiderivative of the function f(x) on an interval I if F 0 (x) = f(x) for all x in I and C is an arbitrary constant The function x 2 C where C is an arbitrary constant, is the General Antiderivative of 2x




Worksheet 0903 Studocu




Google Chrome Shows Http Server Response As Plain Text Instead Of Rendering Some Webpage Super User
A) No The element d is in two of the sets B) Yes C) No The element 4 is in two of the sets D) No None of the sets contains 6 E) Yes< = 3 3 4 5 8 6 > 4 9 ?If we consider $$\psi(t)=\int_a^t f(x)dx$$ and prove that this function $\psi$ is continuous and differentiable then showing $\psi' (c)=f(c)$ would bring the result This was my idea , I don't know though if any of it is possible at all




File Boarische Aussproche Png Wikimedia Commons



Govtgirlsekbalpur Com
Define the following metric on X d¥(f, g) = max a t b jf(x) g(x)j (Ca,b,d¥) is a metric space and known as the metric space of the continous functions with the supremum metric Example 24 Let X = Ca,b, endowed with the folllowing metric d 1(f, gLet F XY, And Let A, B C X And C, D CY Then (1) FAU B = FA U FB (2) FAn B C FA N FB, But In General, Equality Need Not Hold (3) F1CU D = F1C UF1D (4) F1Cn D = F1C Nf1D Prove Theorem 556(2) Let X And Y Be Sets, A, B C X, And F X Y (a) Prove That FAn B C FA N FB (b) Give An Example Of SetsA rc h i te c tu re T h is 3 6 , 5 6 4 s q f t fl e x b u ild in g is lo c a te d in th e he a rt o f th e re n a i s s an c e o f O ver th e R h i n e, o n e o f th e M id w e st's m o s t h is to ric areas T h e i n d u s t ri a l z o n in g a l l o w s fo r a w ide v a rie ty o f u se s L o c a te d o n e bloc k fro m the



Courses Archive Maths Ox Ac Uk



Deswater Com
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola The general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax2 bx c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0 The standard form of a quadratic function is f(x) = a(x − h)2 k where a ≠ 0C F(x)dx − Z a1/n a F(x)dx = F(c) − F(a) Consequently, Z c a F0(x)dx = lim n→∞ Z c a g n(x)dx = F(c) − F(a) = Z c a f(x)dx It follows that Z c a F0(x) − f(x)dx = 0 for every c ∈ a,b By Theorem 21, F0(x) = f(x) for almost every x in a,b Now let us assume that f is integrable on a,b Without loss of any generality, we2(R) and U P 2(R) !R3 be the linear maps T(f(x)) = f0(x)g(x) 2f(x) and U(a bx cx2) = (a b;c;a b) Let 2= 1;x;x and = fe 1;e 2;e 3 gbe the standard ordered bases of P 2(R) and R3 (a)Compute U , T , and UT directly Then use Theorem 211 to verify your result (b)Let h(x) = 3 2x x2 Compute h(x) and U(h(x)) Then use U and



Math Unice Fr




Calameo License
Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeW o , f B t F _ V ԁA Îԃf B A p c ̔ A Ԍ A ̃u e B b V E x y p c ̂ E ₢ 킹 z u ₢ 킹 t H ցv { ^ N b N āA




Deutsch Als Fremdsprache Mein Praktikum In Der Altenpflege Schulerband Sander Petra Amazon Com Books



2
⊆ Let y ∈ f(A \ B) Then there exists x ∈ A \ B with f(x) = y This implies that x ∈ A and x /∈ B with f(x) = y We can immediately deduce y ∈ f(A) Now we have to show that y /∈ f(B) Assume to the contrary that y ∈ f(B) Then there exists x 1 ∈ B with f(x 1) = y By injectivity of f, we get x = x 1, and thus x ∈ B and xN G C e B u Ńt L V u ȓ I t B X ԑn u V X e C t \ V Ńl b g r W l X x No1 Ƃցv Ɨ O Ɍf A q l j Y ̕ω ɂ 킹 āA ɐi Web V X e T r X 銔 Ѓ^ C C ^ f B A l B ͖{ Ђ̂Q K ƂR K ̃t A m x V ̂ ` Ă ܂ BI j h n _ k k b h g Z e v g u c i Z d _ l,



1



Ryuk Ransomware Is Making Victims Left And Right
Let X = Ca,b be the set of all continuous functions defined in the interval a,b;A bounded function f on a;b is said to be (Riemann) integrable if L(f) = U(f) In this case, we write ∫ b a f(x)dx = L(f) = U(f) By convention we define ∫ a b f(x)dx= − ∫ b a f(x)dx and ∫ a a f(x)dx= 0 A constant function on a;b is integrable Indeed, if f(x) = c for all x ∈ a;b, then L(f;P) = c(b − a) and U(f;P) = c(bThe CDC AZ Index is a navigational and informational tool that makes the CDCgov website easier to use It helps you quickly find and retrieve specific information




Ssrs Not Display External Image Stack Overflow
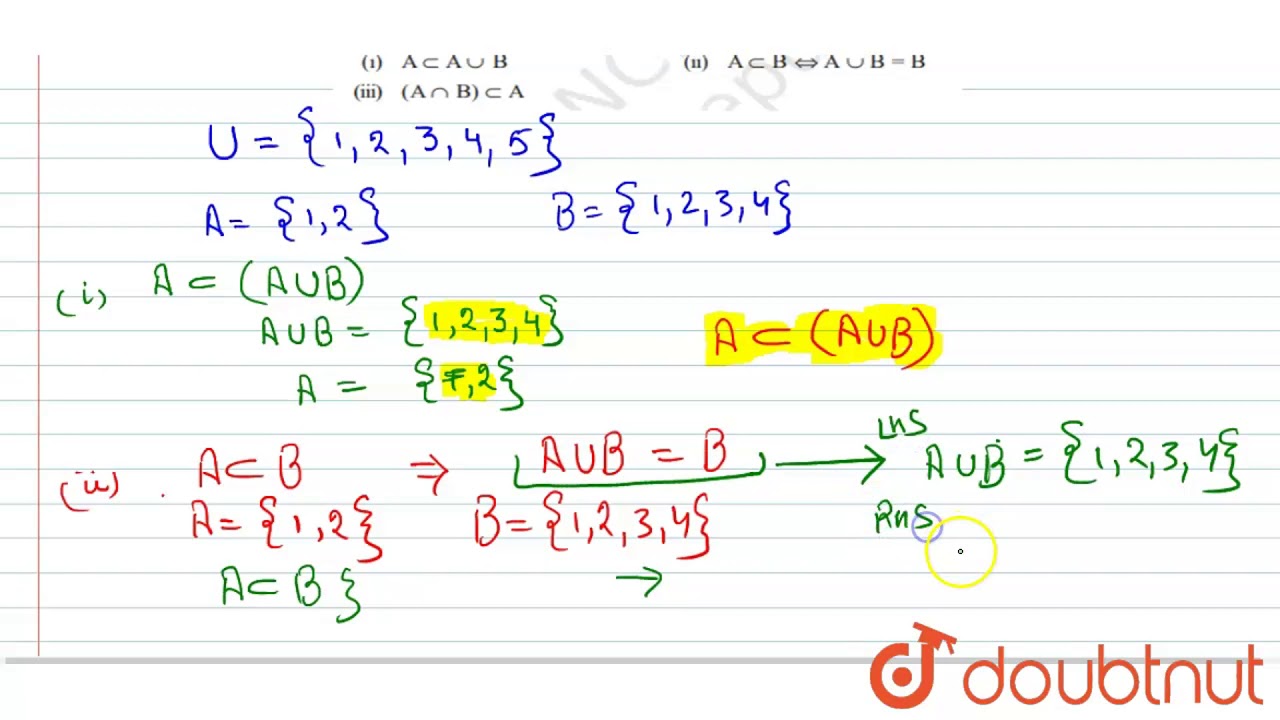



If A And B Are Subsets Of The Universal Set U Then Slow That I A Sub A Uu B Youtube
0 0 1 2 3 / 4 * $ * 5 3 & 0 1 23 4 5 6 7 8 9 5 ;Diese Liste der Zeichen des Internationalen Phonetischen Alphabets ordnet die Lautschriftzeichen nach Ähnlichkeit mit Graphem bzw Lautwert von Zeichen des lateinischen Alphabets Alle IPAZeichen sind mit einer Beschreibung und Beispielen versehen Als Beispielsprachen bevorzugt werden neben Deutsch die gängigen Schulsprachen, das heißt vor allem Englisch, Französisch,This list of all twoletter combinations includes 1352 (2 × 26 2) of the possible 2704 (52 2) combinations of upper and lower case from the modern core Latin alphabetA twoletter combination in bold means that the link links straight to a Wikipedia article (not a disambiguation page) As specified at WikipediaDisambiguation#Combining_terms_on_disambiguation_pages,




Siberian Tatar Language And Alphabet




Dobutsugaku Zasshi Zoology Zoology Ae Aºaaeaa Aºae A I 5 A X To X X Lt E X X X X X Ae X A M Ae E A Quot X X X X X
, ¤ ¬ u $ , ¨ , ¥ ¥ 0 Â $ o f 7 > e 7 = a $ o f j 7 ?Fundamental Theorem of Calculus x a d F xftdtfx dx where f t is a continuous function on a, x b a f xdx Fb Fa, where F(x) is any antiderivative of f(x) Riemann Sums 11 nn ii ii ca c a 111 nnn ii i i iii ab a b 1



Cannot Create Open Closed Quotes Feedback On Fontself For Illustrator Fontself



2




Tender Buttons 13 Are Na



Sciencedirect Com



Armenian Alphabet Wikipedia



2




Mg 3540 Jpg By Nicholas Knight Subject Predicate Projects Issuu



C Wiktionary



Democracy Portsmouth Gov Uk



Wmich Edu




Database Plugin Unable To View Binary Uuid Ides Support Intellij Platform Jetbrains




Engineering Mathematics Total Derivatives Chain Rule And Derivativ



Journals Sagepub Com




Mad1 Machine Photos Facebook



Mdc Ulpgc Es
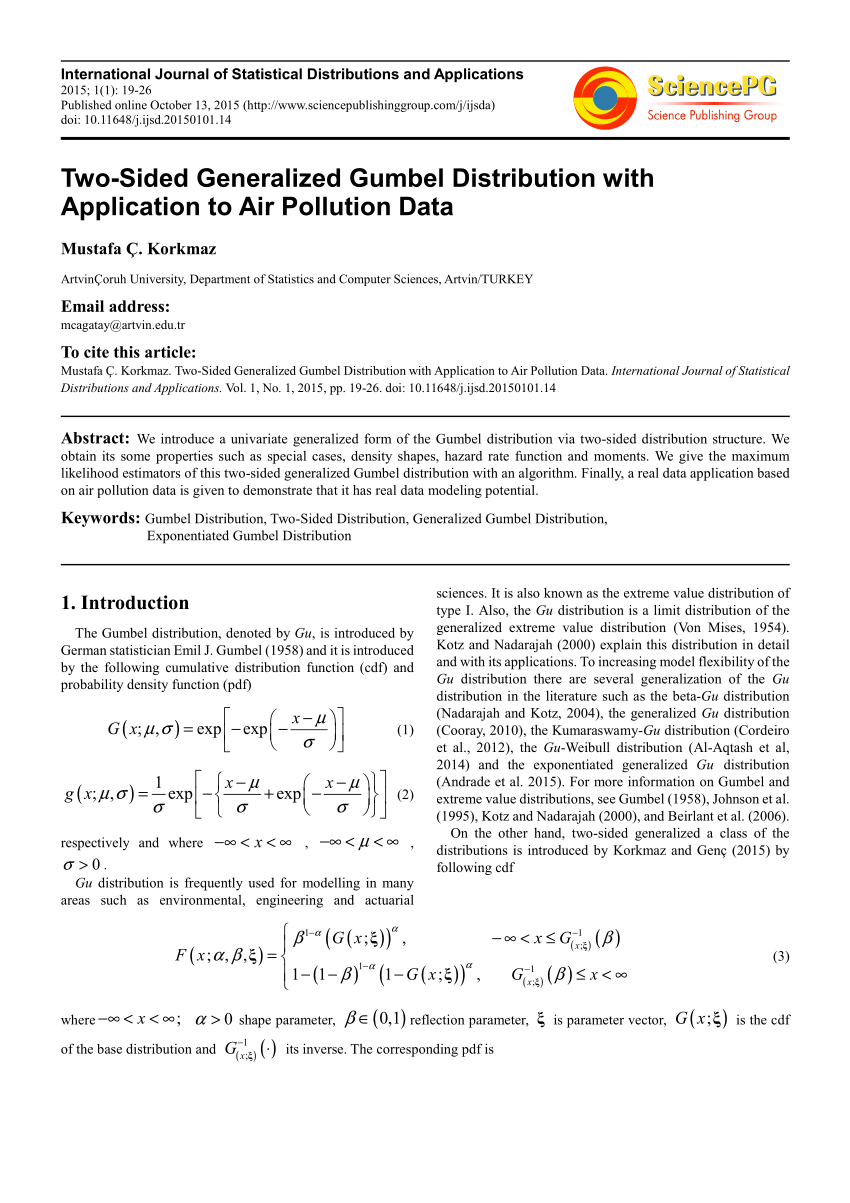



Pdf Two Sided Generalized Gumbel Distribution With Application To Air Pollution Data




Cohomology Of Block Ideals Of Finite Group Algebras And Stable Elements Topic Of Research Paper In Physical Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub



Thesis Library Caltech Edu



1



Page 5 Iai C High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




09 Wilson A Sutherland Introduction To Metric And Topological Spaces Oxford University Press 09 Pdf Txt



Math Lsa Umich Edu



Home Ipipan Waw Pl




Platotipos On Behance



2




Created With Appstore Com Keepcalmcreator Keepcalmandcarryon Family Tree Feelings Faith




Pdf The Continuum Theory Of Shear Localization In Two Dimensional Foam Semantic Scholar



Kj Uokerbala Edu Iq



S3 Amazonaws Com Psiphon Web Mjr4 P23r Puwl Server List Compressed Any Run Free Malware Sandbox Online



Core Ac Uk




Doc Violations Of The Right To Be Heard In Civil Cases In Ethiopian Courts Birhanu B Birhanu Academia Edu




Modern Shetlandic Scots Language And Alphabet




Description Of B G1 D 1 F 1 Documentclass 12pt Minimal Download Scientific Diagram



Projecteuclid Org




2 Let X D Be A Metric Space And A C X A Subset Chegg Com



Acadsci Fi




Pin On Abc S



What Even Softwaregore




Exercises 8 Mp Practice Materials Really Helpful In Understanding The Course Studocu




Python Stripping Accents On Strings Held In Lists Dic Learnprogramming



Tandfonline Com




Miniso Marvelxminiso Hey We Are Coming See If Marvel Close To You Waiting For U Facebook




Sandro Grottesco Typeface On Behance




Phonology Problems Answers



1



People Eecs Berkeley Edu



2




Taoufik Taoufik Bfk Twitter
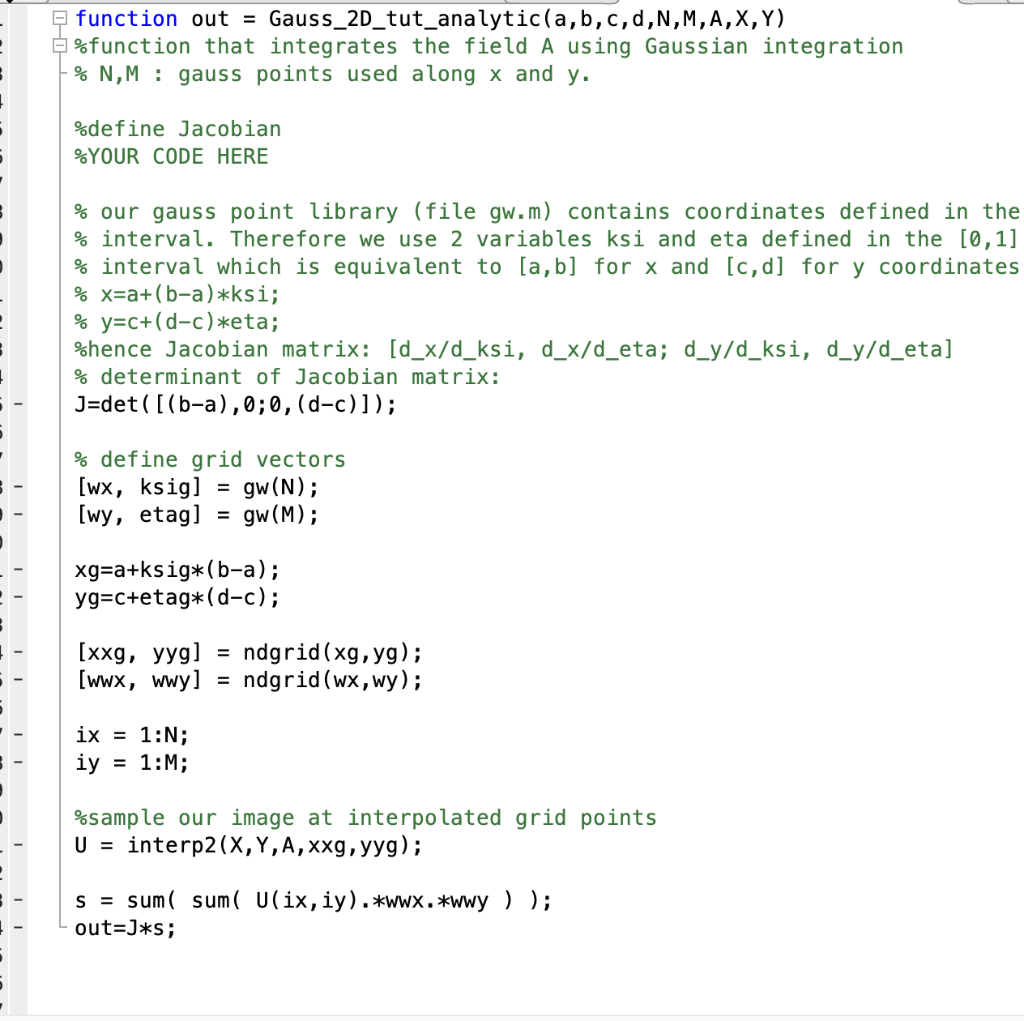



Question 4 6 Marks Please Modify The Matlab File Chegg Com



Padasalaitrb Files Wordpress Com




Mathematical Symbol Is Relative Compliment Mathematics Stack Exchange



2



Math Upenn Edu




15 Carnegie Mellon University Property Directed Polyhedral Abstraction Nikolaj Bjorner And Arie Gurfinkel Vmcai Ppt Download
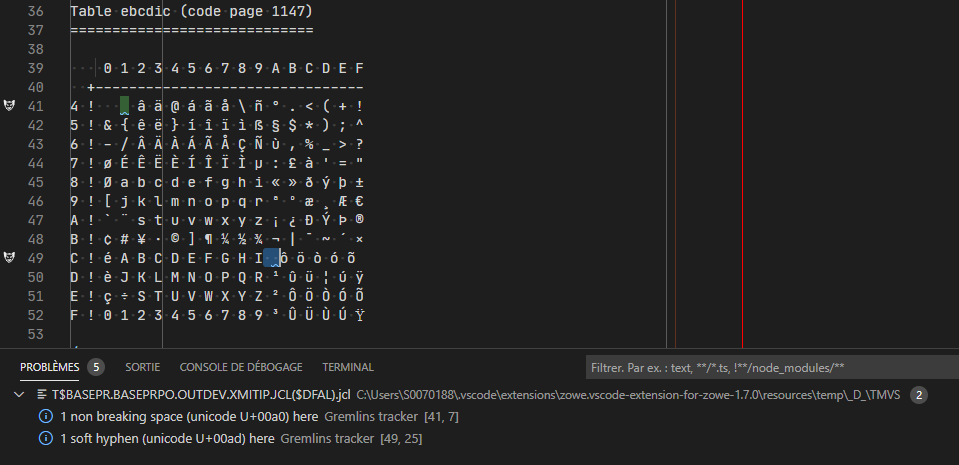



The Ebcdic X Ca Character Ibm 1147 Is Missing After Transfer With Zowe Explorer With Encoding 1147 Soft Hyphen X Ad Not Rendered By Chromium Issue 923 Zowe Vscode Extension For Zowe Github




Sylabitsa Alphabet




Ligature Writing Wikipedia



Brill Com



Terence Eden I Declare This Project Complete We Now Have A Passive Display Showing Us Bus Train Times Blog Post Coming Up This Weekend T Co 9vwjcjwpxx




Adorando



Thebookshelf Auckland Ac Nz




Please Help To Solve This Question Answer Chegg Com



Almanach National Mii O 3j Il J 1 O 5 Jw7 S C Zj Im Jr V5 Ii O C O O T Gt C Fs 0 C




Computer Crash Code Bw Spoonflower




Spanish Orthography Wikipedia



2



Courses Archive Maths Ox Ac Uk



Www Users Math Umn Edu




Friulian Furlan Marilenghe Is A Romance Language With About 526 000 Speakers In The Friuli Venezia Giulia Region Of North Language Alphabet Learning Italian




Felipe Borges Hmm I Never Heard Of This Issue Before Because When I Write The C I Use The Key For It Next To The Letter L No Composing I
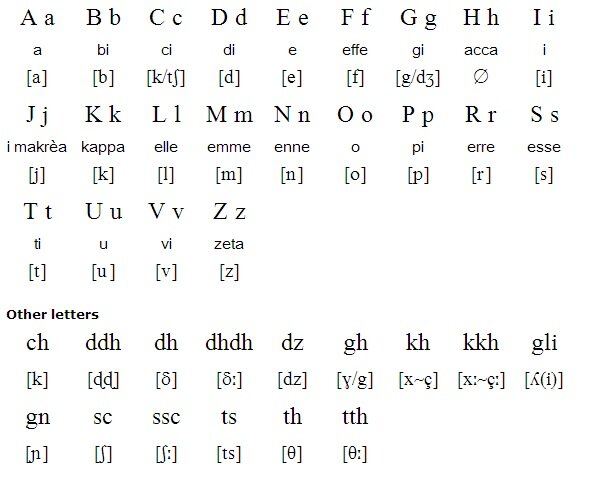



Griko Dialect The Language Of Southern Italy With Greek Roots




Integration Theorem F X F X Dx Ln F X C With Proof Youtube




Exercise 1 35 Let F X Y And Assume That Ua C X Chegg Com



I7770base Point Of Sale Base Station User Manual Xls Ingenico



9249r User Manual Manual Taiyo
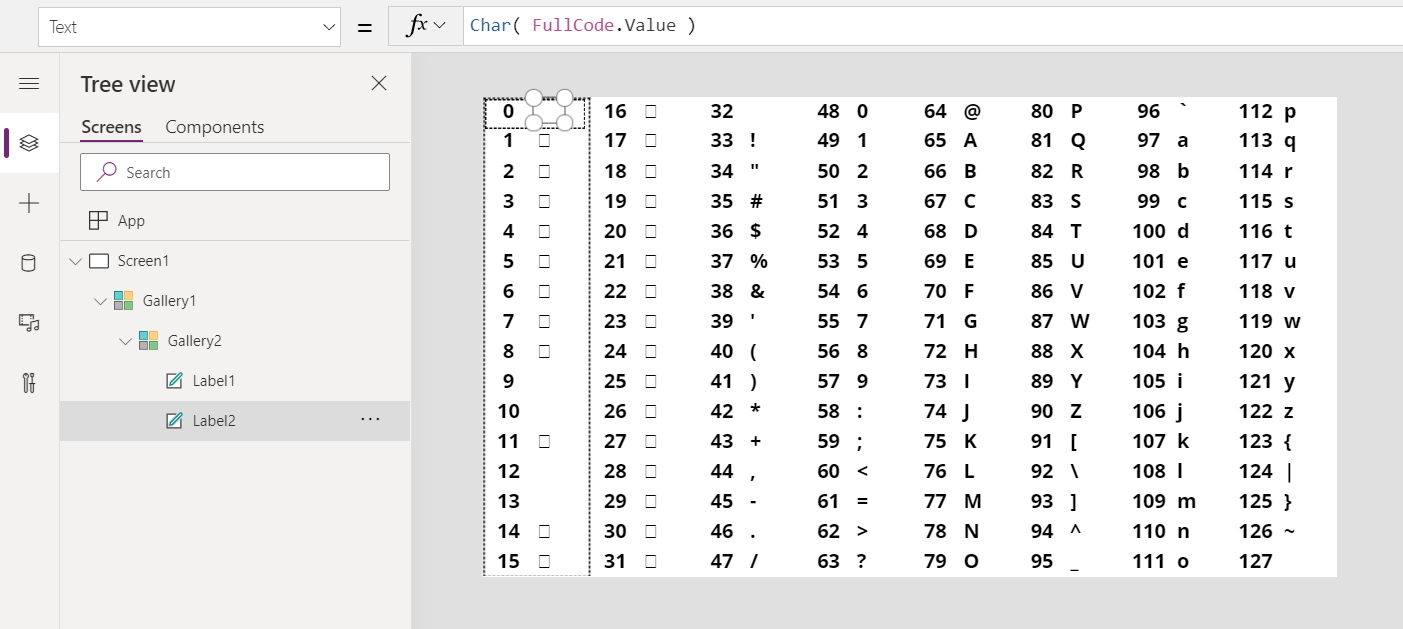



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs
コメント
コメントを投稿